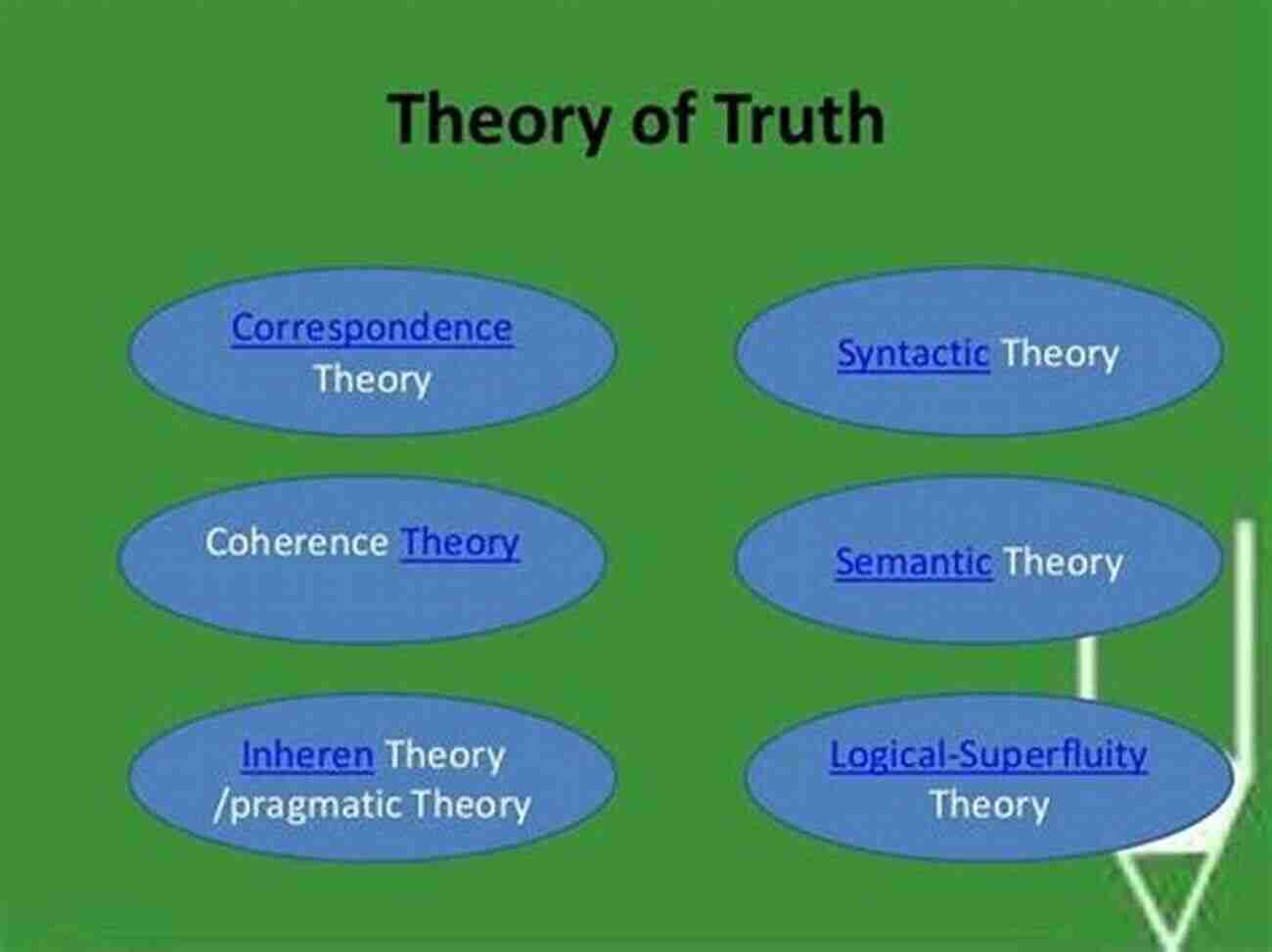
Truth has always been a subject of immense fascination and debate within the realm of philosophy. Enlightenment thinkers, such as Descartes, Kant, and Hegel, delved into the depths of the human mind to explore the true meaning of truth. Their philosophical inquiries sought to unearth the fundamental nature of reality and knowledge.
The Search for Truth
For centuries, philosophers have grappled with questions like: What is truth? Does it exist objectively or is it merely a subjective construct? How can we differentiate truth from mere belief or opinion?
Renowned philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle gave birth to the foundational concepts that initiate the quest for truth. Socrates stated, "An unexamined life is not worth living." Plato emphasized the existence of a higher reality beyond our sensory perceptions, while Aristotle focused on the pursuit of knowledge as the key to understanding the truth.
4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 4621 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 297 pages |
Throughout history, philosophers have presented various theories and perspectives on truth. Rationalism suggests that truth can be derived through reason and critical thinking. Empiricism, on the other hand, asserts that truth is acquired through our sensory experiences.
The Subjectivity of Truth
One of the most intriguing aspects of truth in philosophy is its subjectivity. While truth is often associated with objectivity and universality, philosophers have explored the notion that truth can be highly individual and subjective.
Niels Bohr, a prominent physicist and philosopher, argued that our observation of reality is intrinsically linked to our perspective. He believed that truth is shaped by the observer and influenced by their unique experiences and cultural background.
This subjectivity of truth raises questions about the existence of an absolute truth. Can there be one ultimate truth that encompasses all perspectives, or are truths merely relative to individual interpretations?
The Importance of Truth in Society
Truth plays a crucial role in society. It forms the foundation of trust, justice, and morality. In the legal system, for example, truth-seeking is essential for ensuring fair judgments and maintaining social order.
Furthermore, truth is an integral part of scientific progress. Scientists strive to uncover empirical truths through rigorous experimentation and observation. The pursuit of truth in scientific endeavors has led to groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in various fields.
Truth also shapes our personal lives and relationships. Honesty and authenticity are often revered as virtues, reinforcing the significance of truth in our daily interactions.
The Philosophical Dilemmas of Truth
Despite its importance, truth remains elusive, tantalizing philosophers with paradoxes and dilemmas. One such dilemma is the Liar Paradox, famously exemplified by the statement, "This sentence is false." If this statement is true, then it must be false.
Another intriguing dilemma is the idea of subjective perception. How can we be certain that our personal perceptions and experiences align with the objective truth? Is it possible to escape the limitations of subjectivity?
Truth and Postmodernism
In recent decades, postmodernist thinkers have challenged traditional notions of truth. Postmodernism emphasizes the social and cultural construction of reality, arguing that truth is a product of power dynamics and linguistic frameworks.
Postmodern thought highlights the multiple interpretations and narratives that exist within a society, suggesting that truth is not fixed, but rather a constantly shifting concept. This perspective has both provoked controversy and expanded the philosophical discourse surrounding truth.
The Continuing Quest for Truth
Despite the complexities and contradictions surrounding truth, philosophers and thinkers continue to explore its vast and profound implications. The search for truth remains essential to our understanding of ourselves, the universe, and the very nature of existence.
As we delve deeper into the realm of philosophy, it becomes apparent that the meaning of truth is as vast and varied as the philosophical theories themselves. The quest for truth is an ongoing journey, constantly challenging our perceptions and expanding our understanding of the world around us.
From ancient wisdom to contemporary debates, truth continues to captivate our minds and push us to question the nature of reality. It is through this intellectual exploration that we uncover the truly great meaning of truth in philosophy.