















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
The Porphyrins V1 Structure And Synthesis Part: Unlocking the Secrets of these Fascinating Molecules

If you have ever marveled at the intricate beauty of a red rose or been captivated by the vibrant colors of a stained glass window, you have witnessed the magic of porphyrins. These complex molecules, found abundantly in nature, play a crucial role in various biological processes. In this article, we will delve deep into the structure and synthesis of these fascinating compounds, unraveling the mysteries they hold along the way.
What are Porphyrins?
Porphyrins are a class of large, rigid, and planar cyclic compounds made up of four pyrrole rings interconnected by methine bridges. The central atom of a porphyrin molecule is typically a metal ion, most commonly iron, magnesium, or zinc. The coordination of the metal ion with the surrounding atoms gives rise to the unique properties of different porphyrins.
It is the porphyrin's ability to complex with metal ions that facilitates its role in various biological functions. For example, in the heme group present in hemoglobin, iron coordination allows for oxygen transport in our blood. Similarly, the magnesium-coordinated porphyrins, known as chlorophylls, play a critical role in photosynthesis - the process through which plants convert sunlight into energy.
4.1 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 59372 KB |
| Print length | : | 663 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Structure of Porphyrins
The core structure of a porphyrin consists of four pyrrole rings, each containing five carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom. These pyrrole rings are linked together by methine bridges, resulting in a highly stable and planar macrocycle. The size and shape of the porphyrin ring can vary depending on the number and position of substituents attached to it.
The central metal ion, which binds to the nitrogen atoms of the pyrrole rings, gives porphyrins their unique properties. The coordination sphere around the metal ion can further extend the aromaticity of the porphyrin ring, enhancing its stability and reactivity. This combination of features makes porphyrins crucial in various biological and catalytic processes.
Synthesis of Porphyrins
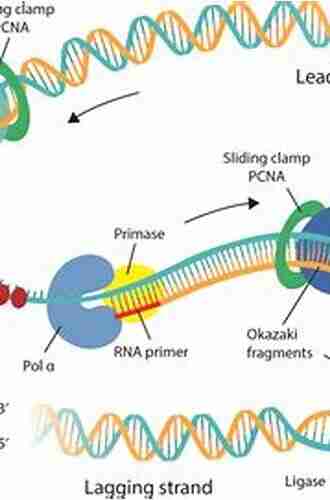
The synthesis of porphyrins is a complex and intricate process. It requires careful control of reaction conditions and involves multiple steps. One widely used method for the synthesis of porphyrins is the Rothemund synthesis, also known as the "classical method."
In the Rothemund synthesis, pyrrole and an aldehyde (such as benzaldehyde) are brought together in the presence of a condensing agent, usually p-toluenesulfonic acid. The reaction proceeds via a series of electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, leading to the formation of porphyrin intermediates. These intermediates then undergo further oxidation, reduction, and metal coordination reactions to yield the desired porphyrin.
Apart from the traditional Rothemund synthesis, several other methods, including the Lindsey method and the Adler-Longo method, have been developed for the synthesis of specific porphyrins and modified porphyrin structures.
Applications of Porphyrins
The unique properties of porphyrins and their versatile structures have opened up a wide range of applications in various fields. One of the most well-known applications is their use as photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy (PDT). Porphyrins can absorb light energy and transfer it to oxygen, leading to the generation of reactive oxygen species that can selectively destroy cancer cells.
Porphyrins also find applications in catalysis, particularly in metalloporphyrin catalysts. These catalysts can facilitate a wide range of chemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, and hydrogenation, due to their ability to coordinate with metal ions and activate them for desired reactions.
In addition to their medical and catalytic applications, porphyrins have also found use in materials science, where they are employed in dye-sensitized solar cells and organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). These applications highlight the significance of understanding the structure and synthesis of porphyrins to develop advanced technologies.
The world of porphyrins is vast and intriguing. From their role in oxygen transport and photosynthesis to their applications in various scientific fields, porphyrins continue to captivate researchers and scientists. By understanding their complex structure and mastering their synthesis, we can unlock the true potential of these incredible molecules. Whether in the realm of medicine, catalysis, or materials science, porphyrins hold great promise for shaping our future.
The mesmerizing beauty of nature's colors and the potential for groundbreaking technological advances lie within these fascinating porphyrin molecules. Embrace the journey of discovery and unlock the secrets of these remarkable compounds today!
4.1 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 59372 KB |
| Print length | : | 663 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
The Porphyrins, Volume I: Structure and Synthesis, Part Ais the first in a series of seven volumes and covers topics like nomenclature, purification, and structural determination of porphyrins, metalloporphyrins, and other related compounds. This volume serves to be a critical review of the topics covered and presents a complete and comprehensible discussion on the chemistry and biochemistry of porphyrins.
The chapters in the text tackle the history and geochemistry of porphyrins and related systems. Also covered and discussed in the chapters is the synthesis of porphyrins from mono-, di-, and tetrapyrrolic intermediates. The isolation and modification of porphyrins from natural sources are also discussed. Other related compounds are also included, such as metallo-, aza-, and N-methylporphyrins, and their synthesis and properties.
This book is a good and reference for students studying in the fields of chemistry and biochemistry.

 Samuel Ward
Samuel WardTake Control Of Your Network Marketing Career
Are you tired of working...

 Bryson Hayes
Bryson HayesThe Enigmatic Talent of Rype Jen Selk: A Musical Journey...
When it comes to musical prodigies,...

 Norman Butler
Norman ButlerUnveiling the Rich History and Poetry of Shiraz in...
When it comes to the cultural...

 Cade Simmons
Cade SimmonsHow Impatience Can Be Painful In French And English
: In today's fast-paced world, impatience...

 William Shakespeare
William ShakespeareSewing For Sissy Maids - Unleashing Your Creative Side
Are you ready to dive...

 Harry Hayes
Harry HayesGST Compensation to States: Ensuring Fiscal Stability...
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic,...

 Rodney Parker
Rodney ParkerLearn How to Play Blackjack: A Comprehensive Guide for...
Blackjack, also known as twenty-one, is one...

 Wade Cox
Wade CoxComplete Guide Through Belgium And Holland Or Kingdoms Of...
Welcome, travel enthusiasts, to a...

 Jack Butler
Jack Butler15 Eye Popping Projects To Create with Felt Decorations
Felt decorations have become a popular craft...

 Dennis Hayes
Dennis HayesFirst Aid For Teenager Soul Mini Book Charming Petites...
The teenage years can...

 Brett Simmons
Brett SimmonsFrom Fear To Freedom - Overcoming Your Fears and Living a...
Are you tired of living in...

 Carl Walker
Carl WalkerSmoking Ears And Screaming Teeth: The Shocking Truth...
Smoking has long been known to cause a host of...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Bob CooperHow American Football Explains Turkey - An Engaging Journey through Cultural...
Bob CooperHow American Football Explains Turkey - An Engaging Journey through Cultural...
 Junichiro TanizakiThe Ultimate Basic Baseball Guide For Kids | Step into the World of America's...
Junichiro TanizakiThe Ultimate Basic Baseball Guide For Kids | Step into the World of America's...
 Adrian WardFive Dark Fates: Unveiling the Gripping Conclusion to the Three Dark Crowns...
Adrian WardFive Dark Fates: Unveiling the Gripping Conclusion to the Three Dark Crowns...
 Allen ParkerInnovative Military Logistics From Lake George To Khe Sanh Modern War Studies
Allen ParkerInnovative Military Logistics From Lake George To Khe Sanh Modern War Studies Dallas TurnerFollow ·7.9k
Dallas TurnerFollow ·7.9k Desmond FosterFollow ·11.3k
Desmond FosterFollow ·11.3k Abe MitchellFollow ·14.7k
Abe MitchellFollow ·14.7k Thomas PynchonFollow ·15.3k
Thomas PynchonFollow ·15.3k Justin BellFollow ·18.9k
Justin BellFollow ·18.9k Luke BlairFollow ·4.4k
Luke BlairFollow ·4.4k Raymond ChandlerFollow ·3.4k
Raymond ChandlerFollow ·3.4k Ignacio HayesFollow ·14.8k
Ignacio HayesFollow ·14.8k