















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Unveiling the Wonders of Electromagnetism

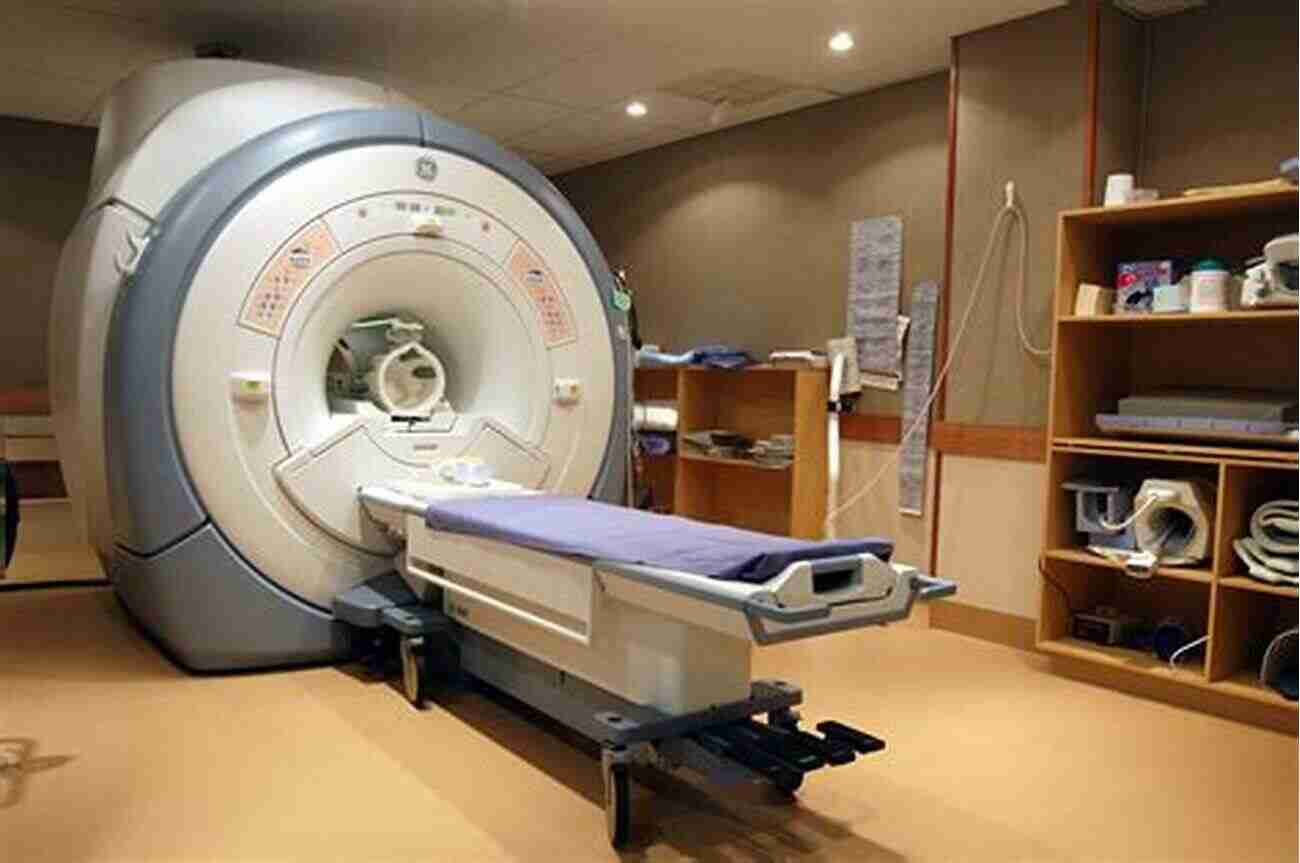
Have you ever wondered how doctors are able to visualize the inner workings of your body without invasive procedures? One technology that has revolutionized the field of medical diagnostics is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). In this article, we will delve deep into the physical principles and applications of MRI, specifically focusing on the role of electromagnetism in this remarkable technology.
The Discovery and Evolution of MRI
The first MRI scanner was developed in the early 1970s by a team of physicists and engineers led by Dr. Raymond Damadian. The technology was initially named Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR),but the word "nuclear" was later dropped to avoid political and public sensitivities. Since then, MRI has undergone significant advancements, becoming an invaluable tool for diagnosing a wide range of medical conditions.
Principles of Electromagnetism
Before diving into the intricacies of MRI, let's briefly explore the fundamental principles of electromagnetism. Electromagnetism is the branch of science that deals with the interaction between electrically charged particles and magnetic fields. It encompasses the concepts of electric charge, electric field, magnetic field, and their interrelationships.
4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2515 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 182 pages |
Electromagnetic waves, such as light and radio waves, are composed of electric and magnetic fields oscillating perpendicularly to each other. These waves have various properties, including frequency, wavelength, and amplitude, which determine their behavior and interaction with matter.
The Role of Electromagnetism in MRI
So, how does electromagnetism come into play in the context of Magnetic Resonance Imaging? MRI relies on the principles of electromagnetism to create detailed images of a patient's internal structures such as organs, tissues, and blood vessels. It harnesses the behavior of atomic nuclei in the presence of strong magnetic fields and radiofrequency pulses.
The first step in an MRI scan involves placing the patient inside a large cylindrical magnet, which produces a powerful static magnetic field. This field aligns the atomic nuclei within the body, primarily targeting hydrogen nuclei, which are abundant in water and fat molecules.
Once the nuclei are aligned, small radiofrequency pulses are applied, causing the nuclei to resonate or "flip." This resonance is a result of the nuclei absorbing and then releasing energy at a specific frequency determined by the magnetic field strength. The emitted radiofrequency signals are picked up by sensitive receivers, allowing the creation of detailed spatial and temporal images.
Applications of MRI
MRI has become an essential imaging modality in various medical fields, owing to its high resolution, versatility, and non-invasive nature. Here are some of its key applications:
1. Neuroimaging
MRI enables detailed visualization of the brain and spinal cord, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions such as tumors, strokes, multiple sclerosis, and neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's disease.
2. Musculoskeletal Imaging
Injuries to bones, joints, and soft tissues can be accurately assessed using MRI. This makes it a valuable tool for detecting fractures, ligament tears, and abnormalities in tendons, cartilage, and muscles.
3. Cardiac Imaging
MRI allows for comprehensive evaluation of the heart's anatomy and function. It provides insights into congenital heart diseases, myocardial infarction, and other cardiac conditions.
4. Oncological Imaging
By capturing detailed images of tumors and surrounding tissues, MRI helps in the detection, staging, and monitoring of various cancers. It aids in treatment planning and assessing response to therapy.
The Future of MRI
As technology continues to advance, the future of MRI looks promising. Researchers are working on enhancing image quality and reducing scan times. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop specialized MRI techniques to address specific clinical challenges.
One such advancement is functional MRI (fMRI),which measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood oxygenation. This technique has opened new avenues for studying cognitive processes, mapping brain functions, and understanding mental disorders.
, Magnetic Resonance Imaging has revolutionized the field of medical diagnostics, providing a non-invasive and detailed look into our bodies. By exploiting the principles of electromagnetism, MRI has become an indispensable tool for diagnosing a wide range of medical conditions. With ongoing research and technological advancements, the future of MRI holds even greater potential for improving healthcare outcomes.
4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2515 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 182 pages |
This book is intended as a text/reference for students, researchers, and professors interested in physical and biomedical applications of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Both the theoretical and practical aspects of MRI are emphasized. The book begins with a comprehensive discussion of the Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) phenomenon based on quantum mechanics and the classical theory of electromagnetism. The first three chapters of this book provide the foundation needed to understand the basic characteristics of MR images, e.g.,image contrast, spatial resolution, signal-to-noise ratio, common image artifacts. Then MRI applications are considered in the following five chapters. Both the theoretical and practical aspects of MRI are emphasized. The book ends with a discussion of instrumentation and the principles of signal detection in MRI.
- Clear progression from fundamental physical principles of NMR to MRI and its applications
- Extensive discussion of image acquisition and reconstruction of MRI
- Discussion of different mechanisms of MR image contrast
- Mathematical derivation of the signal-to-noise dependence on basic MR imaging parameters as well as field strength
- In-depth consideration of artifacts in MR images
- Comprehensive discussion of several techniques used for rapid MR imaging including rapid gradient-echo imaging, echo-planar imaging, fast spin-echo imaging and spiral imaging
- Qualitative discussion combined with mathematical description of MR techniques for imaging flow

 Samuel Ward
Samuel WardTake Control Of Your Network Marketing Career
Are you tired of working...

 Bryson Hayes
Bryson HayesThe Enigmatic Talent of Rype Jen Selk: A Musical Journey...
When it comes to musical prodigies,...

 Norman Butler
Norman ButlerUnveiling the Rich History and Poetry of Shiraz in...
When it comes to the cultural...

 Cade Simmons
Cade SimmonsHow Impatience Can Be Painful In French And English
: In today's fast-paced world, impatience...

 William Shakespeare
William ShakespeareSewing For Sissy Maids - Unleashing Your Creative Side
Are you ready to dive...

 Harry Hayes
Harry HayesGST Compensation to States: Ensuring Fiscal Stability...
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic,...

 Rodney Parker
Rodney ParkerLearn How to Play Blackjack: A Comprehensive Guide for...
Blackjack, also known as twenty-one, is one...

 Wade Cox
Wade CoxComplete Guide Through Belgium And Holland Or Kingdoms Of...
Welcome, travel enthusiasts, to a...

 Jack Butler
Jack Butler15 Eye Popping Projects To Create with Felt Decorations
Felt decorations have become a popular craft...

 Dennis Hayes
Dennis HayesFirst Aid For Teenager Soul Mini Book Charming Petites...
The teenage years can...

 Brett Simmons
Brett SimmonsFrom Fear To Freedom - Overcoming Your Fears and Living a...
Are you tired of living in...

 Carl Walker
Carl WalkerSmoking Ears And Screaming Teeth: The Shocking Truth...
Smoking has long been known to cause a host of...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Colt SimmonsThe Fifty Year Seduction: Unveiling the Remarkable Tale of Love, Deception,...
Colt SimmonsThe Fifty Year Seduction: Unveiling the Remarkable Tale of Love, Deception,...
 Isaac AsimovThousand Sunny Days with Rachel Mullins: The Enchanting Tale of Perseverance...
Isaac AsimovThousand Sunny Days with Rachel Mullins: The Enchanting Tale of Perseverance...
 Shannon SimmonsHow to Turn Fans Into Customers And Customers Into Fans: The Ultimate Guide
Shannon SimmonsHow to Turn Fans Into Customers And Customers Into Fans: The Ultimate Guide Vernon BlairFollow ·9.4k
Vernon BlairFollow ·9.4k Douglas AdamsFollow ·3.3k
Douglas AdamsFollow ·3.3k Joshua ReedFollow ·15.6k
Joshua ReedFollow ·15.6k Phil FosterFollow ·5.7k
Phil FosterFollow ·5.7k Sammy PowellFollow ·4.3k
Sammy PowellFollow ·4.3k Ricky BellFollow ·12.9k
Ricky BellFollow ·12.9k Dwight BlairFollow ·16.9k
Dwight BlairFollow ·16.9k Grayson BellFollow ·10k
Grayson BellFollow ·10k